Data Goes Circular
Topic outline
-
-
Welcome! 👋
Please read this course introduction before starting.
This course will provide you with the basic knowledge in data science and sustainability through summaries, videos and some questions we have prepared for you. It will take you approx. between 3 - 5 hours depending on your speed of reading, selection of videos and your individual learning depth.
Here you will be taken on a journey through the beginnings and definition of sustainability, current ESG issues and reporting standards, learn what the Sustainable Development Goals are, and dive into the circular economy, shared economy, and greenwashing.
We have also prepared some use cases to help you understand data-driven circular business models and teach you the basic concepts of data science. Through the Circular Data Service Cards developed by TU Graz, Know Center and oikos Consulting, we hope it will be easier for you to understand the topics around data sources, data analytics, data services, benefits and circular strategies.
You will also find some additional resources at the end of the course. The small quizzes after each lesson will help you reflect on what you have learned, so be sure to read the content to be able to answer them.
With that in mind, we hope you have a great learning journey! 🚀 -
👉 To enhance your learning experience and learn from Peers, feel free to write your questions in this forum or share your interested topics around sustainability and data science and knowledge with others!
-
You will find latest great opportunities, news and online events around those topics to further continue your learning journey in this announcements section! 👍
So stay tuned! 😎
-
-
-
Sustainability is a very broad concept that englobes interconnected subjects. Indeed, to define this world it is important to understand that sustainability is a combination of the three following pillars that are dependant and interconnected: economic sustainability, social sustainability and environmental sustainability.
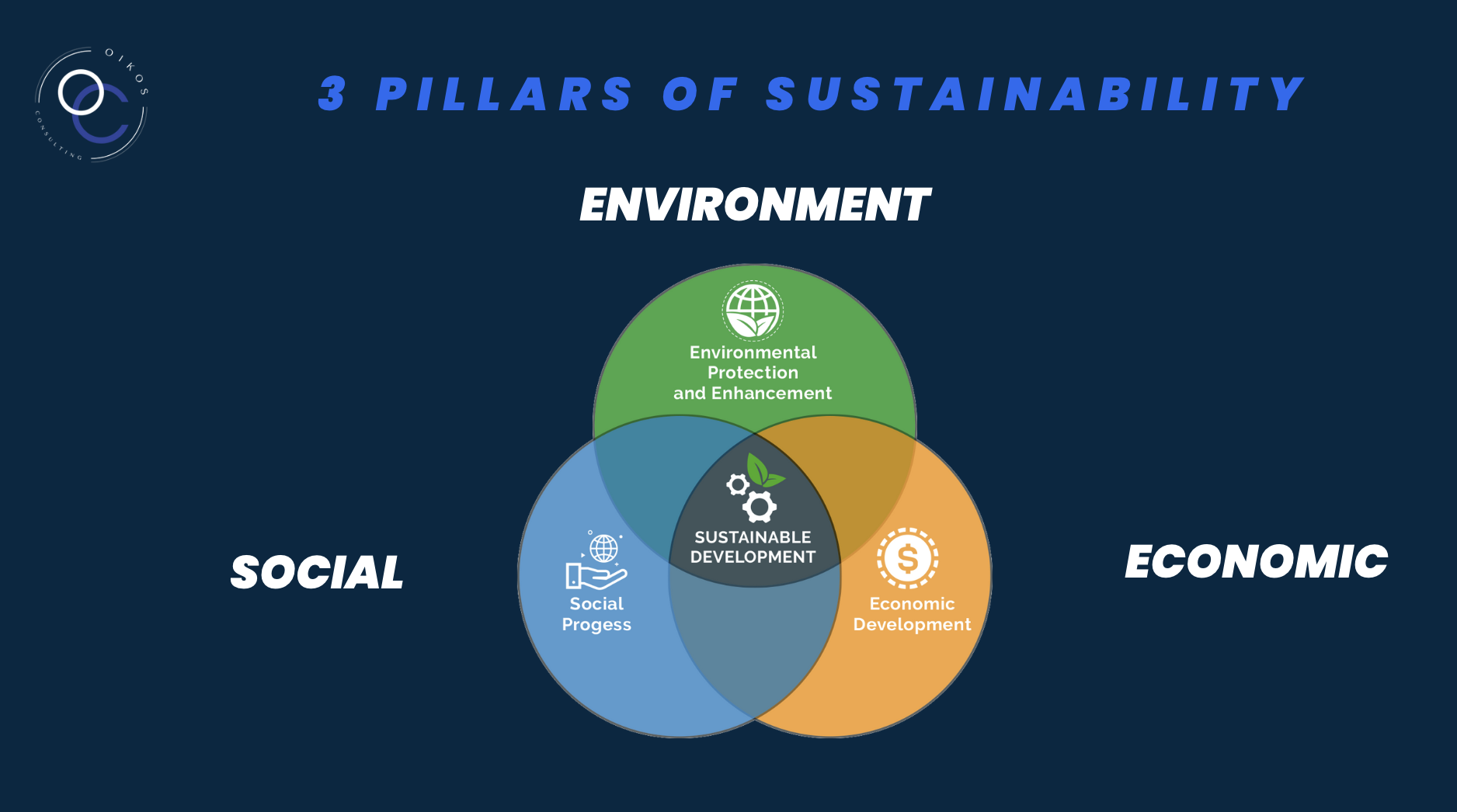
-
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) are a set of 17 goals established and set by the United Nations in 2015. Their establishment is part of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. These goals are related to the three pillars of sustainability described in the previous chapter, thus covering economic, social and environmental aspects. They provide a comprehensive framework for addressing the world's greatest challenges, such as poverty, inequality, climate change, environmental degradation, and social injustice. This initiative encourages active sustainable action and engagement by all stakeholders.

-
An effective way to ensure sustainable practices and avoid greenwashing is to ensure that information is disclosed in a consistent, transparent and credible manner. Reporting standards help to meet these expectations by providing guidance and frameworks for organisations to report on their economic, social and environmental (ESG) performance and progress. By adhering to sustainability reporting standards, organisations can legitimise their actions and increase their sustainability credibility.
This lesson provides a general overview of the sustainability reporting standards that currently exist.
-
The circular economy is an economic model that aims to achieve sustainability goals. It is an integral part of sustainability management and appears to be a sound approach to tackling global challenges such as climate change, waste management and the management of limited resources.
In this lesson you will learn the basics of circular economy, get some examples and learn how to design it.

-
The shared economy or the sharing economy is based on the principle of collaborative and more sustainable consumption. This is an economic model that can be included as an integral part of the circular economy model. It actively promotes the concept of resource optimisation by sharing, renting, and using under-utilised resources and assets. The goal of this model is to reduce environmental impact by reducing waste, extending product lifespan while promoting access to ownership for everyone, developing social relationships within communities and producing economic benefit.
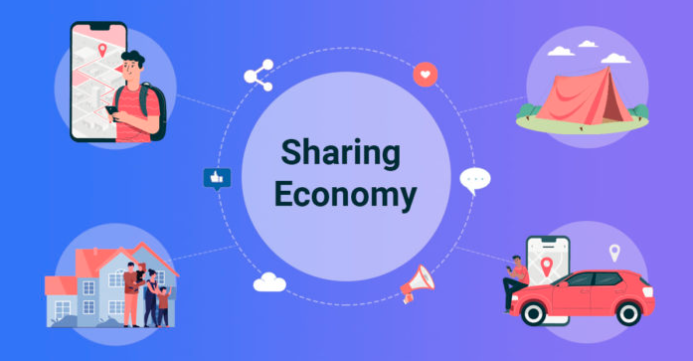
-
Greenwashing a marketing or public relations strategy used by organisations to create a misleading image of being environmentally responsible, green or sustainable. This results in a lack of genuine commitment to sustainability, generally characterised by a lack of transparency, vague, irrelevant or incomplete claims, hidden trade-offs of so-called 'sustainable measures', and certifications or labels without substance. One way to avoid this practice is to develop reporting standards, third-party certification and critical thinking.
In this lesson we will show you examples for greenwashing for a better understanding.

-
Every sector of activity needs to take into account the importance of sustainability and think about an active ESG strategy to promote and put it into practice. According to the sector of the organisation, common sustainable practices, regulations and standards may differ a lot. For this reason, It is important to define and understand the key stakes of sustainability in a given sector.

-
Universities have become one of the main key stakeholders in sustainability management. More and more universities appear as key actors of sustainability efforts through their education, research, operations, and community engagement. Their main actions include curriculum integration, research and development, campus operation such as waste management and sustainable procurement, and community engagement through social actions, student associations such as oikos.

-
-
-
Use cases of real companies that have implemented sustainable actions are a good illustration of all the notions mentioned and described in this platform. Those use-cases are a good way to show the application of sustainable practices in corporations, their challenges and their benefits. The company studied in those use-cases are BIN-E, To Good To Go, Stella McCartney foundation, Tesla and Buhler.
-
BIN-E is an AI-based smart waste bin, designed for office spaces and smart buildings, enabling them to achieve efficiency in waste management and reach green strategy goals. It sorts and compresses the waste automatically, controls the fill level and processes data for convenient waste management. The smart waste bin recognizes the type of waste thanks to an AI-based Recognition System and sorts it to the relevant chamber. The collection service gets notified automatically when one of the bins inside is full. An integrated IOT- Platform provides valuable insights into waste management operations that can be used to optimize collection routes, and save costs, time and labour of waste disposal. It enables the recovery of high-quality raw material and the reduction of CO2 emissions of waste transport.

-
Too Good To Go is the certified B-Corp and tech-for-good company powering the world’s #1 marketplace for surplus food. The app connects consumers to extra food that would otherwise be thrown away from local restaurants, cafes, bakeries and grocery stores, such as pastries, fresh produce, sushi and more. Too Good To Go provides a simple way for food businesses to redirect their surplus, and consumers to help fight climate change in a fun, delicious way. The company’s sales representatives work according to territories. Access to market sizing and penetration data allowed the team to understand how to split their attention across locations, allowing for efficient and effective allocation of time and resource. Access to Local Data Online provides the Sales team with the locations and contact details of potential business partners, allowing them to create targeted lists that can be exported and used for planning outbound sales activity.
-
Tesla a leading electric vehicle (EV) manufacturer leverages data analytics and machine learning to continuously optimize the performance and lifespan of their electric vehicle (EV) batteries. Tesla collects a wealth of data from its EV fleet, including information about battery health, charging patterns, temperature, and driving behavior. This data is analyzed to gain insights into how different factors affect battery performance, efficiency, and degradation over time. By understanding these patterns, Tesla is making informed decisions regarding battery design, chemistry, and management. And also, by analyzing data on battery health, performance, and remaining capacity, Tesla identifies batteries suitable for repurposing and integrate them into energy storage products. This not only extends the lifespan of the batteries but also contributes to a more sustainable energy ecosystem by utilizing renewable energy efficiently and reducing the need for new battery production. Tesla´s data on battery performance enables them to recover valuable materials, such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel, from end-of-life batteries. By implementing recycling initiatives, Tesla reduces reliance on mining, conserves resources, and minimizes the environmental impact associated with raw material extraction.
-
Bühler is a global technology company that specializes in process engineering and solutions for various industries, including food and feed processing, advanced materials, and mobility. Bühler's MoisturePro is a powerful moisture management solution that leverages data-driven insights to optimize moisture control in the food processing industry. By ensuring precise moisture measurements, facilitating process optimization, reducing waste, and enhancing product quality, MoisturePro helps minimize product defects and waste by ensuring precise moisture control throughout the production process. With accurate moisture measurements and real-time data analysis, operators can take corrective actions promptly, reducing product rejections and waste. MoisturePro offers traceability features that enable the recording and tracking of moisture data over time. This facilitates reporting and documentation for quality control purposes, audits, and compliance with industry regulations. MoisturePro helps food manufacturers achieve operational excellence and drive sustainable practices.
-
Stella McCartney Cares Green is a non-profit, charitable platform with a focus on sustainability in fashion. Google cloud and the Foundation are collaborating together to build a tool that uses data analytics and machine learning on Google Cloud to give brands a more comprehensive view into their supply chain, particularly at the level of raw material production. One of the ways they are embracing circularity in their materials and collections is through biological materials, such as cotton, cellulose and wool, each chosen due to the scale of their production, data availability and impact considerations. They are including data sources that allow companies to better measure the impact of their raw materials, relevant to key environmental factors such as air pollution, greenhouse gas emissions, land use and water scarcity. The tool will provide actionable insights to make better raw material sourcing decisions with sustainability in mind.

-
Please answer: What could be an additional sustainability use case of AI or data based decision making in the industry of company’s in considerations?
Argue why you have chosen your example and feel free to discuss with your peers.
-
-
-
Data science plays an important role to support and foster advancement in sustainability efforts. It provides tools such as data analytics or machine learning to speed up decision-making, data gathering and innovation, to optimize resource utilisation, and hence to support sustainable practices across various sectors.

-
Big data is a term used to describe vast volumes of data that are too large and complex to be processed using traditional methods. Big data refers to the massive volume and complexity of data, while data science focuses on the methods and techniques used to extract value from that data. Data science encompasses the tools and methodologies employed to analyze and interpret data, while big data represents the scale and characteristics of the data itself. Data science leverages big data to gain insights and solve complex problems, but it also applies to smaller datasets and traditional data sources.

-
To gather a large amount of data for a sustainable purpose, it is important to take into consideration various sources of data and to understand where that data comes from. Data can be classified in two categories: primary and secondary data.
-
 Introduction of those Cards
Introduction of those Cards -
Data analytics is a tool to interpret, analyse and organize data collected from various sources. Organizations and people can gain valuable information from those data and can apply it to tackle sustainability challenges and meet sustainability goals
-
Introduction of those Cards
-
Data services refer to a range of services that involve the management, processing, storage, and analysis of data. These services typically aim to provide businesses and individuals with efficient and secure access to their data, as well as tools and capabilities to extract valuable insights and make informed decisions.
-
Introduction of those Cards

-
Introduction of those Cards
-
Introduction of those Cards

-
Here are some questions for this section!
-
-
-
You are curious about your own Carbon Footprint? 🤓
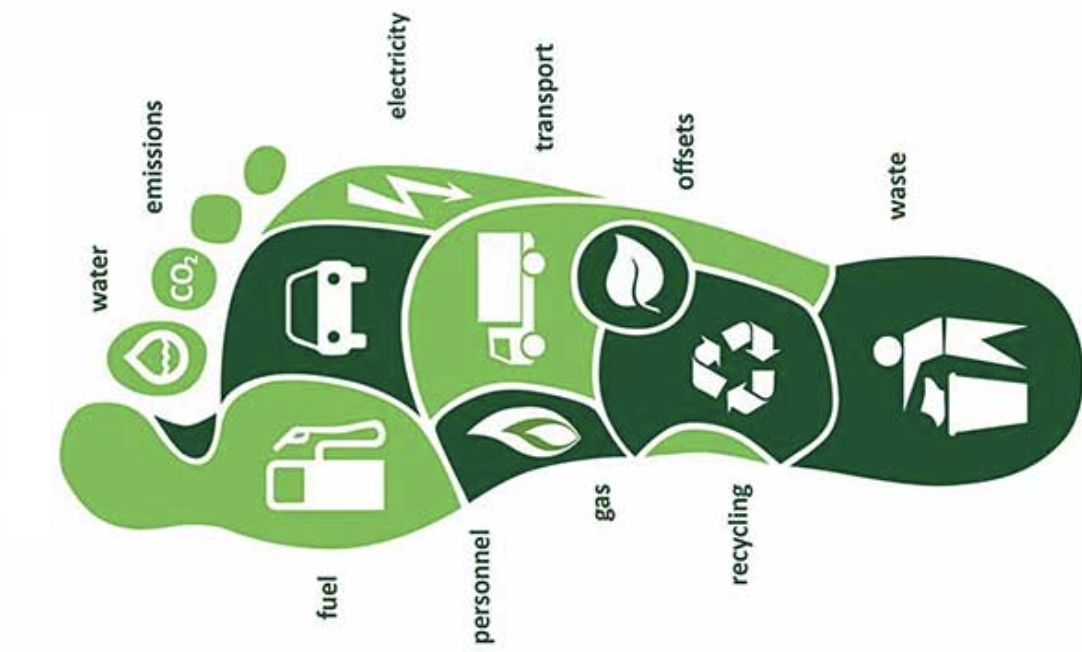
-
Reference Link (further dive into the topic of sustainability reporting)
-
You want to learn more about Data Science and how AI can help our Sustainable Future?

-